Introduction to Arrays and Functions in C
In the world of programming, the C language holds a fundamental position due to its efficiency and low-level capabilities. Among its core concepts, arrays and functions are essential building blocks that enable efficient data management and modular programming. Understanding these concepts is crucial for writing efficient and organized C programs.
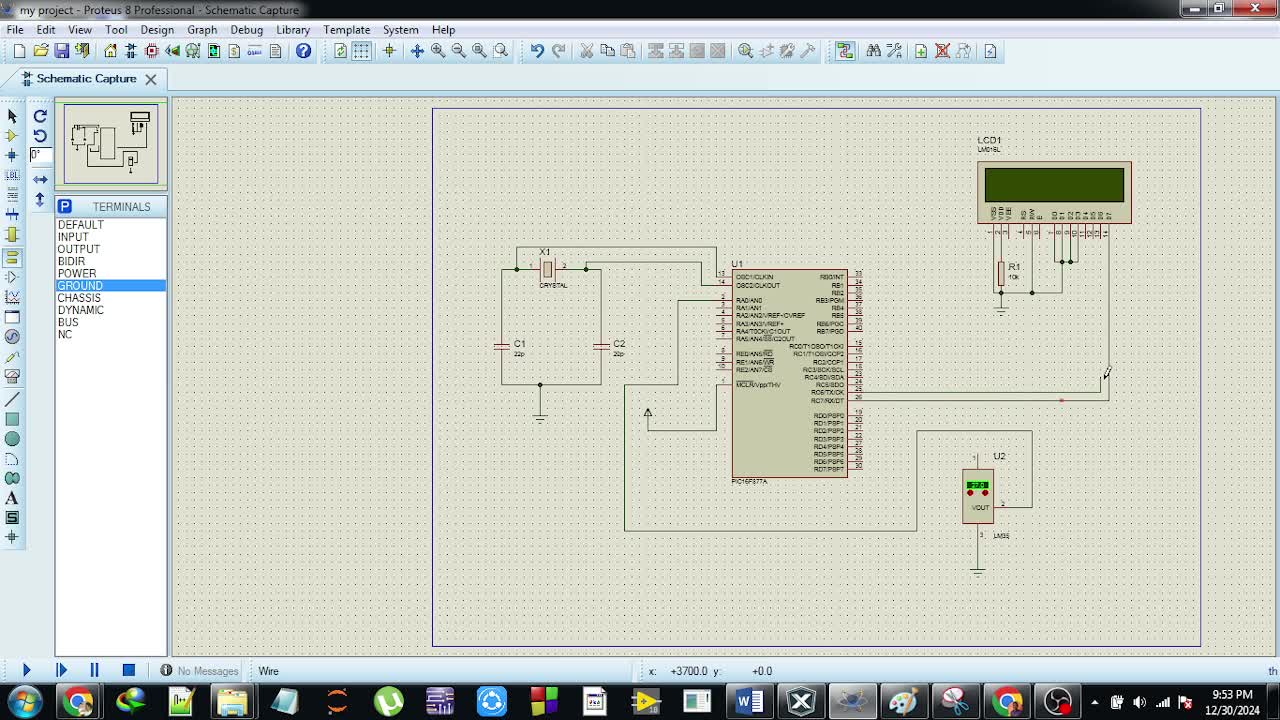
Arrays in C are a collection of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory locations. They provide a way to store and manipulate a large number of data items using a single variable. Arrays can be one-dimensional (like a list) or multi-dimensional (like a matrix), and they are especially useful when dealing with bulk data, such as processing large datasets or managing a collection of similar items. C also supports character arrays, which are used to store and manipulate strings.
Functions, on the other hand, allow for the modularization of code by encapsulating a set of instructions under a single name. This modular approach not only makes programs more organized but also promotes code reusability and maintainability. Functions in C can take inputs, perform specific tasks, and return results, making them highly versatile. The ability to pass arrays as arguments to functions enhances the functionality and flexibility of programs. By passing the array’s base address, C allows efficient manipulation of large data sets within functions without the need to copy the entire array.
The combination of arrays and functions enables programmers to create robust and efficient applications. Whether it’s processing data sets, performing mathematical operations, or managing strings, mastering arrays and functions is fundamental to becoming proficient in C programming. Understanding their synergy is key to writing clean, efficient, and maintainable code.