Your Worksheet is Ready
CBSE - Class 9 Mathematics Circles Worksheet
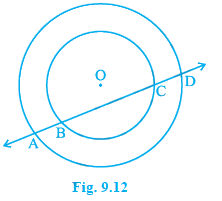
If a line intersects two concentric circles (circles with the same centre) with centre $O$ at $A$, $B$, $C$ and $D$, prove that $AB = CD$ (see Fig. 9.12).
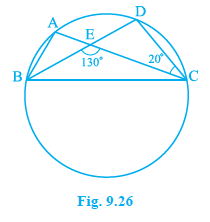
In Fig. 9.26, $A$, $B$, $C$ and $D$ are four points on a circle. $AC$ and $BD$ intersect at a point $E$ such that $\angle BEC = 130^{\circ}$ and $\angle ECD = 20^{\circ}$. Find $\angle BAC$.
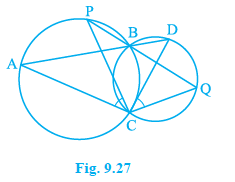
Two circles intersect at two points $B$ and $C$. Through $B$, two line segments $ABD$ and $PBQ$ are drawn to intersect the circles at $A$, $D$ and $P$, $Q$ respectively (see Fig. 9.27). Prove that $\angle ACP = \angle QCD$.
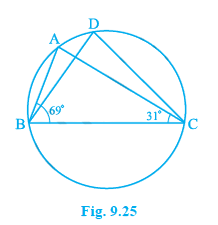
In Fig. 9.25, $\angle ABC = 69^{\circ}$, $\angle ACB = 31^{\circ}$, find $\angle BDC$.
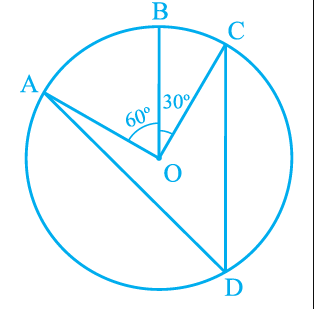
In Fig. 9.24, $\angle PQR = 100^{\circ}$, where $P$, $Q$ and $R$ are points on a circle with centre $O$. Find $\angle OPR$.
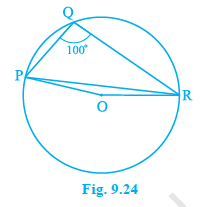
In Fig. 9.23, $A, B$ and $C$ are three points on a circle with centre $O$ such that $\angle BOC = 30^{\circ}$ and $\angle AOB = 60^{\circ}$. If $D$ is a point on the circle other than the arc $ABC$, find $\angle ADC$.
CBSE - Class 9 Mathematics Circles Worksheet
Answers